MonoIS3DLoc
Simulation to Reality Learning Based Monocular Instance Segmentation to 3D Objects Localization From Aerial View
Published in IEEE Access
Key Contributions
- A neural architecture making use of monocular instance segmentation as intermediate representation to indirectly regress 3D object position from RGB aerial images.
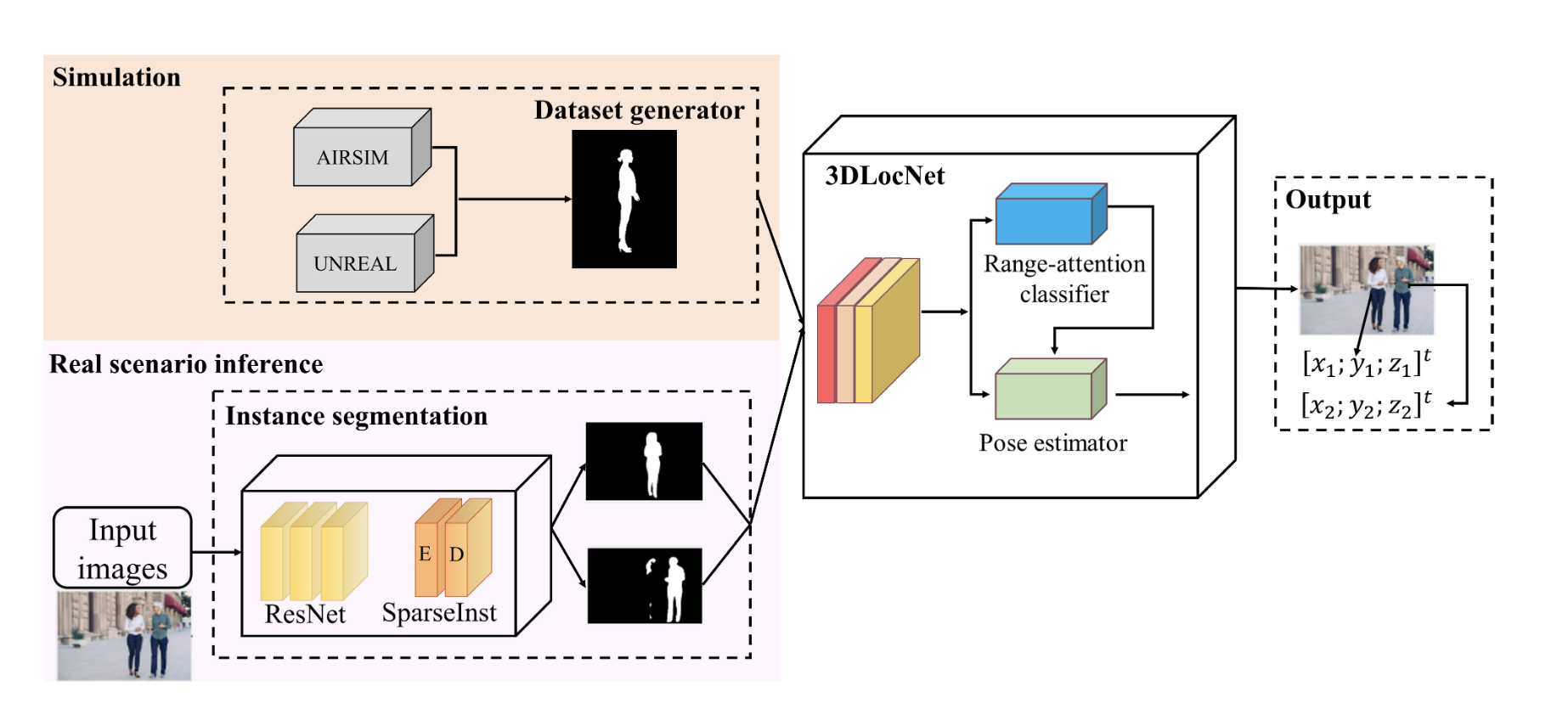
- A new training objective (loss) function to reduce the gap between simulated and real-world data used for training neural pose estimator, without the needs for a robust photo-realistic simulator or domain randomization.
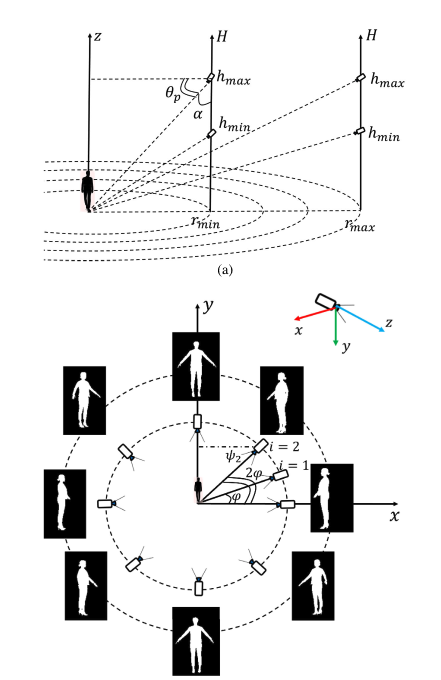
- Data synthesis pipeline using a virtual camera in a simulation environment (AirSim) to collect semantic masks of objects and their corresponding 3D localization information. FOV constraints are applied to ensure the validity and diversity of the 3D localization information.
Acknowledgments
Special thanks to all the co-authors from IVSR Lab and Ritsumeikan's AIS Lab